Understanding the Tarantula Z Axis
The Z axis in your Tarantula 3D printer is a crucial component, responsible for the vertical movement of the print head. It controls the height of the nozzle above the print bed, allowing the printer to build your 3D models layer by layer. Understanding how the Z axis functions is fundamental to achieving successful prints, avoiding common issues, and maintaining your printer for optimal performance. A well-functioning Z axis ensures accurate layer adhesion and overall print quality, making it a vital part of the 3D printing process. Proper setup, calibration, and maintenance of the Z axis will greatly enhance your 3D printing experience.
What is the Z Axis?
The Z axis refers to the vertical axis or the height axis of your 3D printer. It dictates how high or low the print head (the part of the printer that extrudes the filament) is positioned above the print bed. As the printer lays down each layer of filament, the Z axis moves the print head upwards, building the model incrementally. The precision of the Z axis is critical for the accuracy of the final print. A correctly functioning Z axis ensures that each layer is deposited at the correct height, leading to the desired dimensions and structural integrity of your 3D printed object. Any errors in Z axis movement can cause layer shifting, poor layer adhesion, or other print defects.
Why is the Z Axis Important?
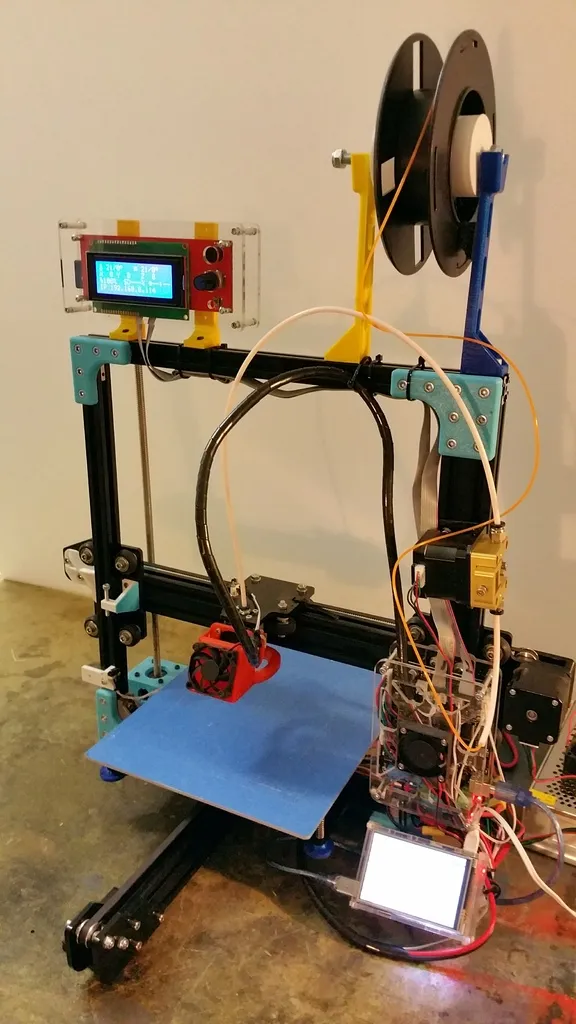
The Z axis is perhaps the single most important axis in 3D printing, since it controls the vertical layering of your print, and determines the final height of your print. Without proper Z-axis functionality, your prints simply won’t be successful. It affects layer adhesion, dimensional accuracy, and overall print quality. If the Z axis isn’t calibrated correctly, layers might not stick together, leading to weak points in the model or even complete print failure. Furthermore, if the Z axis moves too much or too little, the dimensions of the printed object will be incorrect. A properly calibrated and well-maintained Z axis, on the other hand, will lead to precise, strong, and aesthetically pleasing 3D prints.
Components of the Tarantula Z Axis
The Tarantula Z axis comprises several key components working in unison to facilitate vertical movement. Understanding each element will help you assemble, maintain, and troubleshoot your printer effectively. Each component’s condition and correct function are vital for accurate and reliable 3D printing. Inspect these parts regularly for wear and tear and ensure they are properly adjusted and lubricated to ensure smooth operation. Proper understanding of these components is critical to maintaining a successful 3D printing process.
Z Axis Motor
The Z axis motor, typically a stepper motor, is the driving force behind the vertical movement. It receives commands from the printer’s control board and rotates to move the lead screw or drive the belt system. The motor’s speed and precision are critical for accurate layer deposition. Ensure that the motor is securely mounted and properly connected to the control board. Also, check the motor’s specifications to ensure it’s compatible with the printer’s electronics. Over time, motor performance can degrade. Regular maintenance, including lubrication and checking for any unusual noises, can extend the life of your Z axis motor. Make sure that the wiring is in good condition and that the motor is receiving the correct voltage.
Lead Screw or Belt System
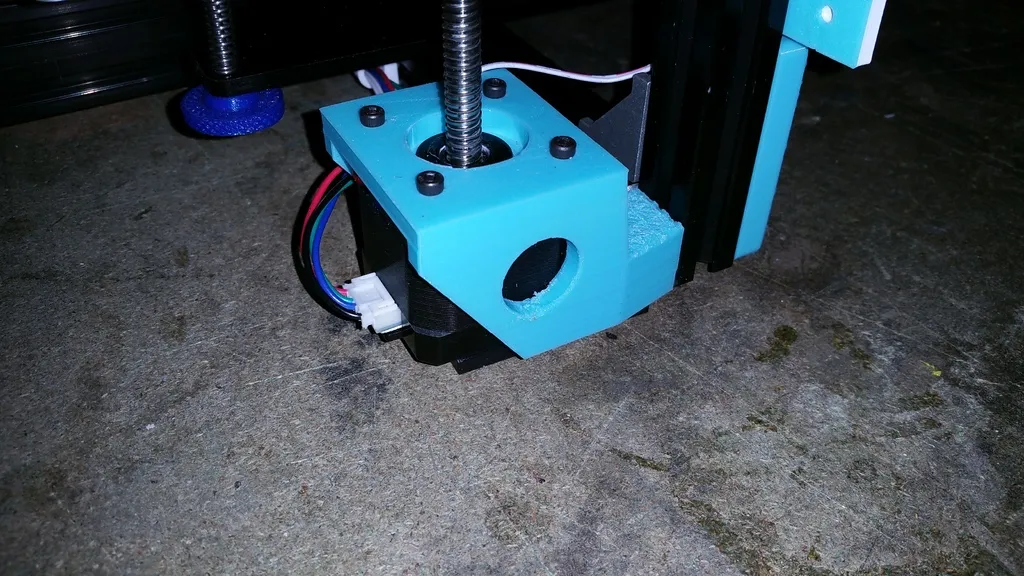
Many Tarantula printers use a lead screw (threaded rod) or a belt system to convert the motor’s rotational movement into linear vertical motion. The lead screw or belt is responsible for translating the motor’s rotation into the precise up-and-down movement of the print head. Regular lubrication of the lead screw is crucial for smooth operation and to prevent wear. Belt systems should be checked for proper tension to avoid slipping, which can lead to printing errors. Depending on the model, it may be an Acme lead screw, which should be lubricated with a high-quality grease to reduce friction and ensure smooth vertical movement. Proper maintenance of this system is essential for achieving consistent layer height.
Z Axis Endstop
The Z axis endstop is a small switch that tells the printer when the nozzle has reached the bed, setting the ‘zero’ point for the Z axis. This ensures the print head starts at the correct height, ensuring the first layer sticks properly. Proper endstop placement is crucial for perfect first layers. If the endstop is not properly set, the nozzle might be too high, causing the filament not to stick, or too low, which can cause the nozzle to scratch the bed. Calibration of the Z axis endstop is a fundamental part of any Tarantula printer setup. Make sure the endstop is securely mounted and properly connected to the control board. Regularly check the endstop’s function to maintain accurate Z-axis positioning. A properly working endstop is essential for the success of your print.
Preparing for Your Tarantula Z Axis Setup
Before diving into the setup process, it is important to prepare your workspace and gather the necessary tools and materials. Taking these preparatory steps will ensure a smooth setup and prevent potential issues during the assembly process. Understanding the required tools and safety measures will not only simplify your setup but also make it a safer experience. Proper preparation is key for a successful Z axis setup, minimizing potential frustrations and ensuring that your printer is ready for use.
Gathering Tools and Materials
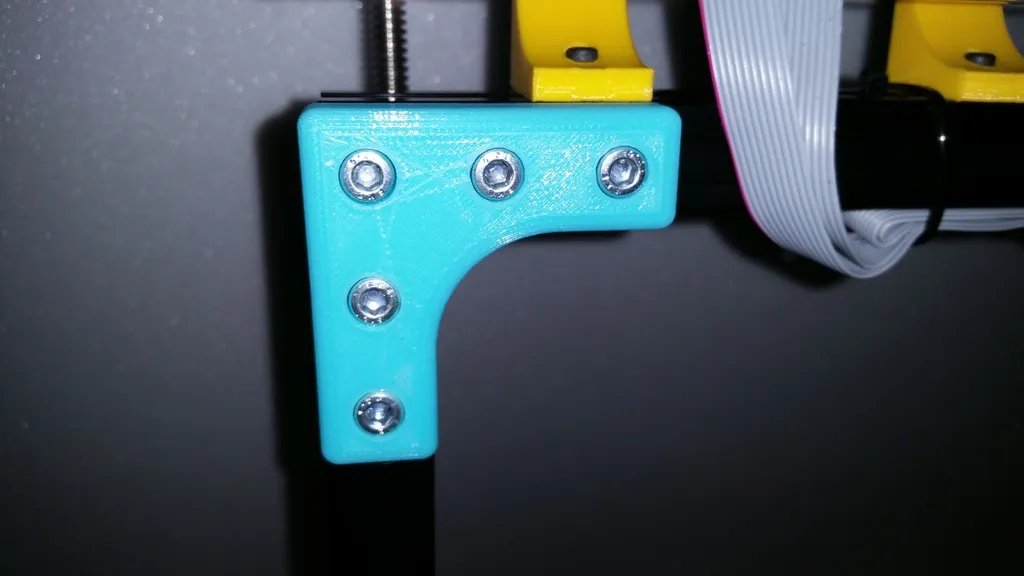

You will need a few tools to set up your Tarantula’s Z axis, including hex keys (Allen wrenches) of various sizes, a screwdriver, and potentially a wrench, depending on your printer’s specific design. Also, have a small ruler or calipers to measure distances, especially when setting up the endstop. You might also need some lubricant, such as lithium grease or silicone lubricant, for the lead screw. Additionally, it’s helpful to have a multimeter for checking electrical connections. Refer to the Tarantula’s manual for any specific tool requirements and ensure you have all the necessary components readily available before starting the setup.
Safety Precautions
Always disconnect the printer from the power supply before working on the electronics or mechanical components. This will prevent any electrical shocks. When handling the Z axis motor and other electrical components, avoid static discharge by touching a grounded metal surface. Be careful with the lead screw or belt system, and ensure that all screws and connections are tightened securely to prevent any mechanical failures during operation. Always consult the user manual for specific safety instructions for your model. Working safely is paramount to prevent injury and ensure the longevity of your 3D printer and personal well-being. If you’re unfamiliar with electrical components, seek assistance from someone knowledgeable before proceeding.
Step-by-Step Z Axis Setup Guide
Follow these steps to correctly set up the Z axis on your Tarantula 3D printer. This process requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure optimal functionality. Taking your time during the setup process will lead to more accurate prints and reduce the need for troubleshooting. Carefully follow the instructions and reference the images to align the components for maximum efficiency. Your 3D printing success depends largely on how accurately you set up your printer’s Z axis. Proper installation is the foundation for high-quality 3D prints.
Mounting the Z Axis Motor

Securely mount the Z axis motor to the printer frame, usually with screws. Ensure the motor is aligned properly and the mounting bolts are tightened. Ensure the motor is level. The motor’s alignment and secure mounting are crucial for preventing vibration during operation and ensuring smooth vertical movement. Make sure the motor shaft is properly coupled to the lead screw or belt system without any binding. Double-check the motor’s stability to eliminate any potential issues later on. If your motor comes with a specific mounting bracket, make sure to install it correctly as per your printer’s instructions.
Installing the Lead Screw or Belt
Carefully install the lead screw or belt system, ensuring it is properly aligned and connected to the motor and the print head carriage. The lead screw or belt should move freely without binding. If you’re using a lead screw, make sure it’s properly threaded into the print head carriage. For a belt system, check for the correct tension. Tighten the belt to the manufacturer’s recommendation for your specific printer model to prevent slipping during operation. Regularly inspect the system for any signs of wear or damage. A well-installed lead screw or belt system is key to smooth and precise vertical movement.
Setting the Z Axis Endstop
Adjust the Z axis endstop to the correct position, usually so the nozzle is just above the print bed when triggered. The endstop tells the printer the zero point for the Z axis. Correct endstop placement is crucial for the first layer to adhere properly. This setting can dramatically affect your print quality. Move the print head down until it gently touches the print bed, then adjust the endstop to trigger at that point. Use a piece of paper between the nozzle and bed to ensure the correct gap for the first layer. After setting, perform a Z-axis calibration test to ensure the settings are appropriate for your printer.
Connecting the Electronics
Connect the Z axis motor and the endstop to the appropriate ports on the control board. Double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and properly wired. Ensure all wiring is properly routed and secured to prevent interference with the printer’s moving parts. Review the wiring diagrams provided with your printer to ensure the correct connections. Verify the connections before applying power to the printer. Using a multimeter to check for continuity will help avoid potential short circuits or incorrect wiring that could damage your printer. Incorrect wiring can cause damage or prevent the Z-axis from functioning.
Calibrating and Testing the Z Axis
Once the Z axis is assembled, it is crucial to calibrate and test it to ensure it’s functioning correctly. Calibration ensures the Z axis moves to the precise positions necessary for accurate layer height. Testing your Z axis confirms that the setup is correct and the printer can perform the intended movements without issues. Proper calibration and testing will dramatically improve the quality of your prints and prevent potential problems. Careful attention to these steps will ensure a properly functioning 3D printer, leading to superior print quality and reliability.
Initial Calibration Steps
Start by leveling the print bed. Make sure the distance between the nozzle and the print bed is consistent across the entire surface. Manually adjust the bed level using the leveling screws or other mechanisms your printer uses. Next, set the Z-offset, which calibrates the distance between the nozzle and the print bed when the Z axis is at its zero position. Many printers have an auto-bed leveling system. After leveling the bed, the Z-offset ensures the first layer adheres correctly. Refer to your printer’s manual for specific instructions and testing methods. The Z-offset is critical for the first layer adhesion and should be adjusted carefully.
Testing the Z Axis Movement
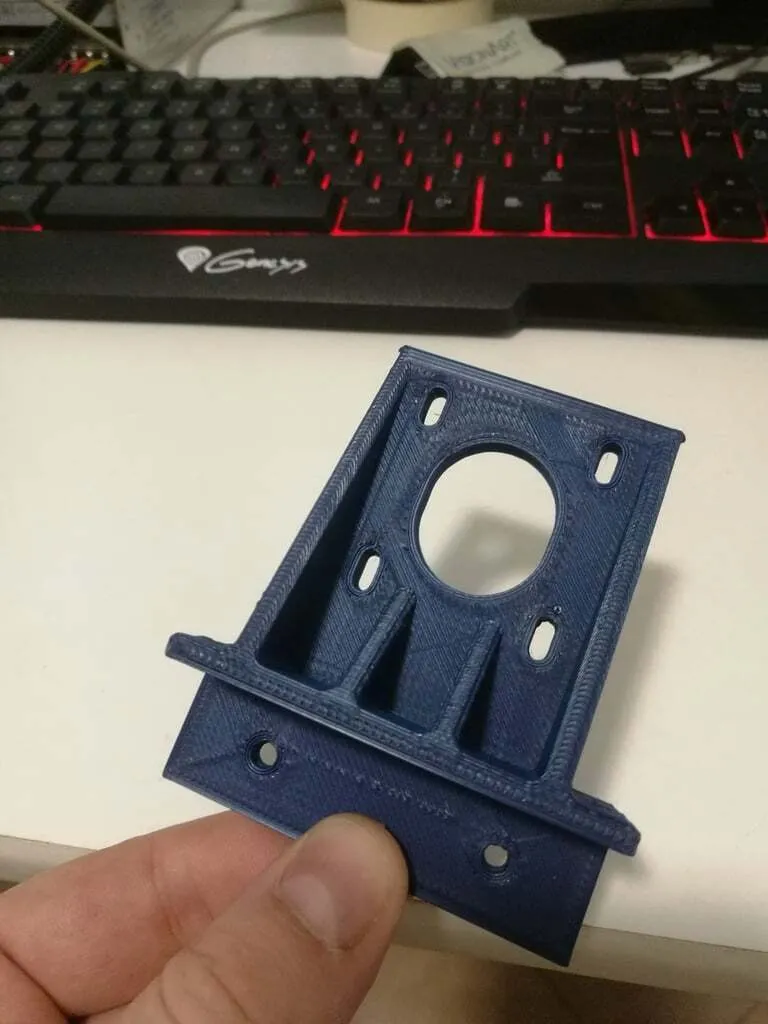

Use your printer’s control panel or software to test the Z axis movement. Command the Z axis to move up and down in small increments, observing the movement closely. Verify that the movement is smooth and consistent, without any binding or unusual noises. Make small adjustments, such as increasing the Z offset if you are experiencing problems, and test the movement again. If your printer has auto-leveling, run the auto-leveling function and observe that the nozzle height adjusts correctly. Regularly check the Z-axis movement, especially after making any adjustments or calibrations. Ensure that the test movements are smooth and accurate, indicating proper calibration.
Troubleshooting Common Z Axis Problems
Even with careful setup and calibration, you may encounter issues with the Z axis. Knowing how to identify and resolve common problems can save you time and frustration. Troubleshooting a Z axis issue requires methodical investigation and testing. By systematically diagnosing the problem, you can efficiently determine the cause and find a solution. Proper maintenance and regular checks can prevent issues and extend the life of the printer. Here are some common problems and their solutions.
Z Axis Doesn’t Move
If the Z axis doesn’t move at all, first check the power supply to the printer and the motor. Ensure the motor is properly connected to the control board and that the connections are secure. Check the motor drivers on the control board; a faulty driver can prevent the motor from functioning. Also, verify that the Z-axis endstop is functioning properly. Make sure that your printer’s firmware is configured correctly for the Z-axis motor and the lead screw or belt system. Test the motor with a different axis motor to see if the motor is the problem. If the motor is not receiving power, inspect the wiring to the motor and the control board for any breaks or shorts.
Z Axis Moves in the Wrong Direction
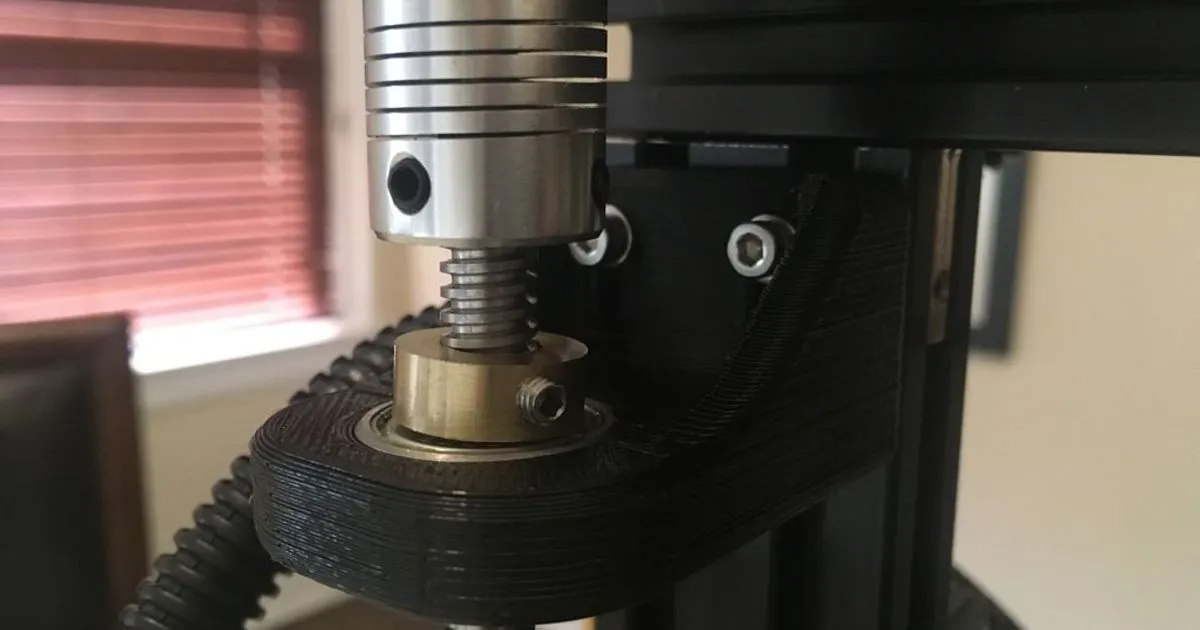

If the Z axis moves in the wrong direction, the motor wires might be connected backward. Swap the motor wires connected to the control board to correct the direction. If you are using the firmware to control the direction of the Z-axis movement, check and adjust the firmware settings. Ensure that the correct settings have been applied. Double-check the motor and wiring; make sure the motor is running in the correct direction as the lead screw turns. Make sure that your printer’s firmware is configured correctly for the Z-axis motor. Sometimes it’s necessary to reverse the direction setting in your printer’s firmware.
Z Axis is Not Level
If the Z axis is not level, the print bed will not be level, which results in print quality problems. The most common cause of an unlevel Z axis is the lead screw or belt not being properly aligned. Ensure that the lead screw or belt is straight and that the motor mount is securely fastened. Check that the Z axis frame is square and aligned. Verify that the print bed is properly leveled. If the bed leveling is not working, make sure that your endstop is correctly adjusted. If all these areas check out and you’re still experiencing problems, you may need to consult your printer’s manual.
Maintaining Your Tarantula Z Axis
Proper maintenance will extend the life of your 3D printer and improve the quality of your prints. Regular upkeep is crucial for the long-term performance and reliability of your Tarantula printer. Consistent maintenance will prevent many of the issues that can arise over time. By following a regular maintenance schedule, you can catch any issues early and prevent them from escalating. Regular maintenance will keep your 3D printer running smoothly and reliably.
Regular Lubrication
Lubricate the lead screw or the moving parts of the Z axis regularly to reduce friction and wear. Use a high-quality lubricant recommended for 3D printers. Apply lubricant according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Excessive lubrication can attract debris. Inspect the lead screw and the print bed carriage, and lubricate those areas to ensure smooth, consistent vertical movement. Applying lubricant helps in reducing friction, which leads to better print quality and long-term reliability. This should be done periodically, based on usage, to ensure your printer runs smoothly.
Checking and Tightening Screws
Periodically check and tighten all screws on your Z axis assembly. Vibration during printing can cause screws to loosen over time. Loose screws can affect the print quality and lead to mechanical failures. Make sure that the motor, lead screw, and other mechanical components are securely fastened. Check the mounting screws of the endstop. Retighten any loose screws to ensure that everything remains in place and functions correctly. Regular inspection and tightening of the screws will greatly improve the overall reliability of your 3D printer.
