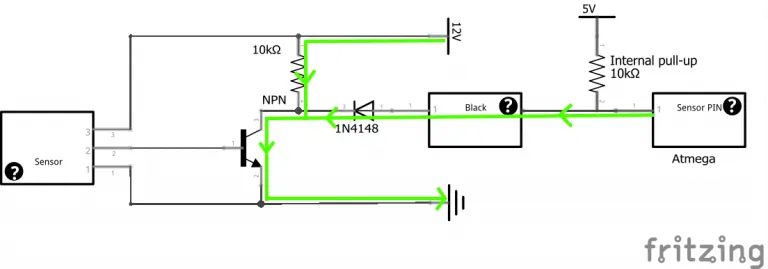
Understanding Auto Bed Leveling on Tevo Tarantula
The Tevo Tarantula, a popular 3D printer, can significantly benefit from auto bed leveling (ABL). This feature automates the process of ensuring the printer’s bed is perfectly level, which is crucial for successful 3D printing. ABL uses a sensor to map the bed’s surface, compensating for any imperfections. This technology drastically reduces the chances of first-layer adhesion problems and ensures more consistent prints. It is a great addition to the Tevo Tarantula, improving print quality and user experience. By understanding how ABL works on the Tevo Tarantula, users can unlock a new level of printing accuracy and reliability.
Why Auto Bed Leveling Matters for Your Tevo Tarantula
Auto bed leveling is a game-changer for 3D printing, especially on a printer like the Tevo Tarantula. It addresses a fundamental challenge: the bed’s flatness. Even the slightest tilt can lead to nozzle-to-bed distance variations, resulting in poor first layers, warping, and failed prints. ABL eliminates these issues by automatically adjusting for bed imperfections. This feature is very crucial for getting a good first layer. It also saves time and frustration by reducing the need for manual bed leveling, which can be a tedious and inaccurate process. Furthermore, ABL ensures optimal nozzle-to-bed distance across the entire print surface, leading to better adhesion and overall print quality.
Common Bed Leveling Issues

Many problems can arise from an unlevel bed. These issues can range from the bed not being perfectly level itself to the sensor’s inaccuracy or incorrect configuration. One of the most common problems is poor first-layer adhesion. If the nozzle is too far from the bed, the filament won’t stick; if it’s too close, the nozzle can drag across the bed, causing issues. Warping is another major problem, where the corners of the print lift off the bed. This is often a result of uneven cooling and poor adhesion. Other issues include inconsistent layer lines, blobs, and overall print failures. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving high-quality 3D prints.
Top 5 Tips for Tevo Tarantula Auto Bed Leveling
Tip 1 Calibration is Key
Calibration is very important for any ABL system to work. Proper calibration ensures that the sensor accurately detects the bed’s surface. This process involves setting the correct Z-offset, which is the distance between the nozzle and the bed when the sensor triggers. Without correct calibration, the printer will either print too close or too far from the bed, leading to problems. Proper calibration will ensure the first layer is correct and the print adheres to the bed, preventing failures.
Why Proper Calibration Matters
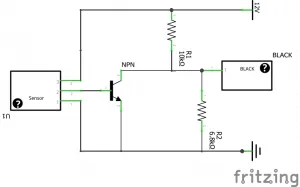
Calibration is not just about setting a value; it’s about ensuring the entire system works in harmony. It affects every aspect of the print, from the initial layer to the final product. Incorrect calibration can result in a host of problems, including poor bed adhesion, nozzle dragging, and overall print failure. It directly influences the quality and accuracy of the prints. When the sensor is properly calibrated, it maps the bed’s surface accurately, allowing the printer to compensate for any imperfections and ensure consistent nozzle-to-bed distance throughout the print.
Calibration Steps
The calibration steps typically involve adjusting the Z-offset until the nozzle is at the correct height for the first layer. This can be done by manually adjusting the Z-offset value in the printer’s settings while printing a test pattern. Most printers have a live Z-offset adjustment during printing. Start by setting the Z-offset to a small value and then increase or decrease it until the first layer looks perfect. The test pattern should have a few lines or squares. This provides a clear visual indicator of how the nozzle interacts with the bed. Repeat this process until the first layer is perfect.
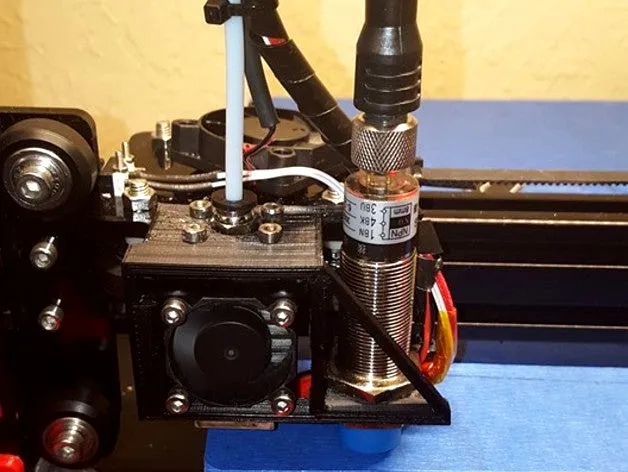
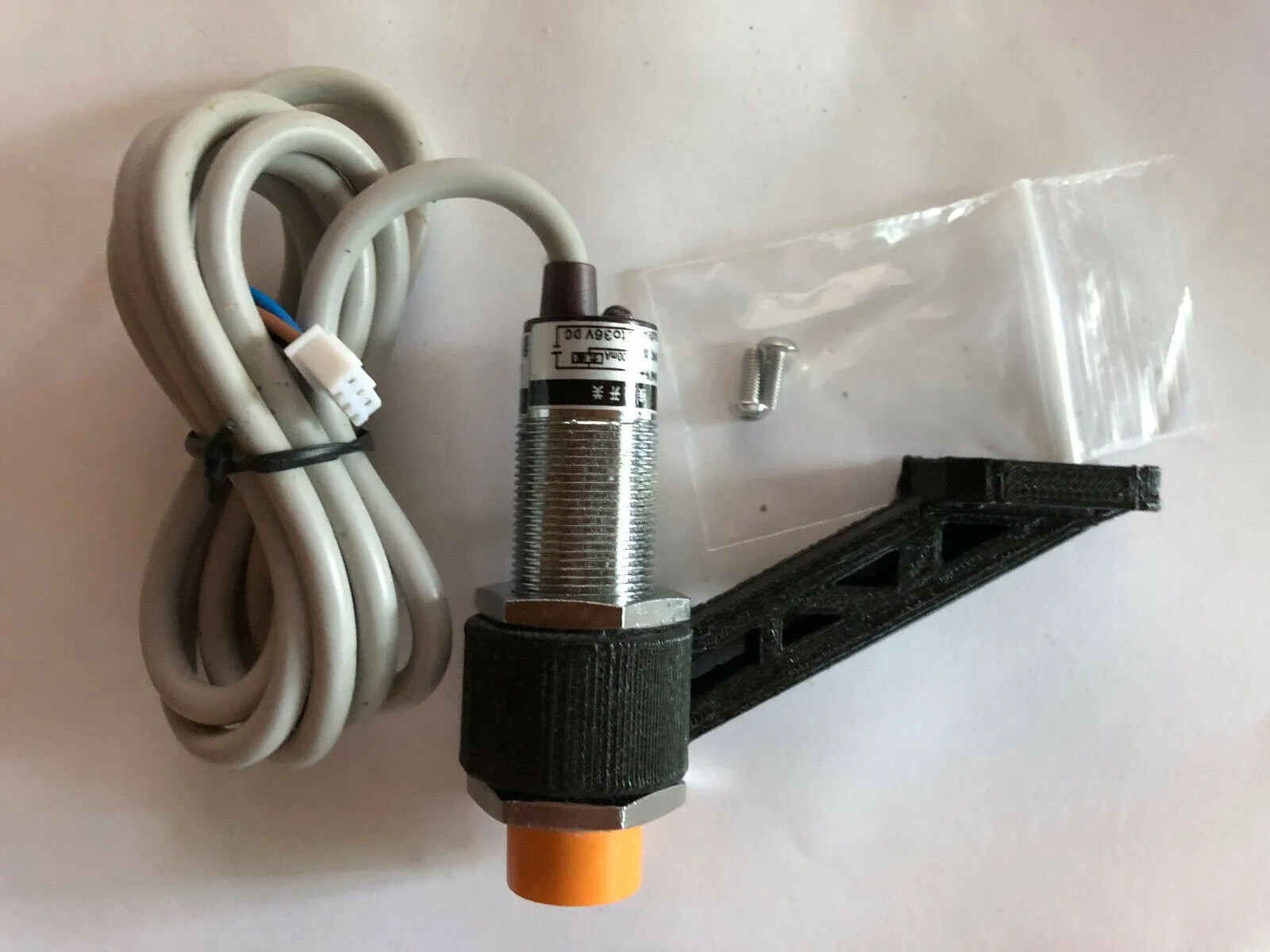
Tip 2 Sensor Placement and Adjustment
The placement and adjustment of the sensor is very important for getting accurate bed leveling. The sensor should be mounted securely and positioned correctly relative to the nozzle. It needs to be far enough from the nozzle to detect the bed surface before the nozzle touches it, but not so far that it misses the bed’s contours. The sensor’s height is very important. It directly affects the Z-offset value, which needs to be set precisely for accurate printing. The sensor needs to be aligned and adjusted properly for it to perform correctly. Proper sensor placement and height adjustment are the fundamentals of successful ABL.
Optimal Sensor Position
The ideal sensor position is slightly offset from the nozzle, typically a few millimeters horizontally. The exact distance depends on the sensor type and mounting system. The sensor should be positioned so it can reliably detect the bed surface without interfering with the nozzle. Consider the sensor’s detection range; it must be able to ‘see’ the bed before the nozzle reaches it. It should not be so far away that it fails to detect the bed’s contours accurately. Most sensors come with specifications that indicate the best placement for optimal performance. A well-positioned sensor can ensure that the printer’s ABL system works effectively, providing accurate bed leveling and improved print quality.
Sensor Height Adjustment
Sensor height adjustment is usually the most important part of the calibration process. The sensor’s height relative to the nozzle is critical for accurate bed leveling. The height of the sensor should be set so that it triggers at the correct distance from the bed. If the sensor is too high, it won’t detect the bed, and the nozzle will crash. If the sensor is too low, it will trigger too early, leading to a Z-offset that is too large, and the first layer won’t adhere correctly. The best way to set the sensor height is using a calibration routine or a Z-offset adjustment. It might be necessary to adjust the sensor height mechanically as well. This could involve loosening screws and moving the sensor up or down.
Tip 3 Firmware Configuration
The firmware of your 3D printer is important, especially when using ABL. It is necessary to enable and configure the ABL features in the firmware. Without the correct settings, the ABL sensor won’t function correctly. You need to configure the firmware to use the sensor, and to understand its readings. The firmware interprets the sensor data, creates a bed mesh, and adjusts the Z-axis height during printing. A crucial part of the process is ensuring the firmware is compatible with the sensor type and correctly interpreting its signals. Updating your firmware is important for getting the newest features, as well as bug fixes. Ensure that the firmware is correctly configured for your specific printer and ABL sensor.
Choosing the Right Firmware

Selecting the right firmware is very important. There are many options available, with Marlin being one of the most popular choices for the Tevo Tarantula. When selecting firmware, check compatibility with the ABL sensor. The firmware needs to have the necessary code to interpret the sensor signals and to use the data to level the bed. Compatibility extends beyond just the sensor type; the firmware also needs to be compatible with the printer’s mainboard and other hardware components. Before installing the firmware, it is helpful to back up your current settings. This can save you from losing all of the configurations. Before installing, make sure to research the firmware version to make sure it is safe and stable.
Configuring Marlin Firmware
Configuring Marlin firmware involves editing the configuration files to enable ABL. You’ll need to uncomment specific lines in the configuration.h and configuration_adv.h files. For example, you’ll enable the features that support your type of ABL sensor. Once you have enabled the ABL feature, you will also need to configure the Z-offset. This tells the printer the distance between the sensor trigger point and the nozzle. This needs to be calibrated and adjusted correctly to get good prints. It also helps to configure the mesh bed leveling settings, such as the grid size and probing speed. Once you have done all the configurations, it is time to compile and upload the firmware.
Tip 4 Bed Adhesion Solutions
Bed adhesion is crucial for successful 3D printing. The first layer is the foundation of every print. Without good adhesion, the print can warp, detach from the bed, and fail. Using auto bed leveling is not enough; you still need to address adhesion. This often involves using adhesives or build surfaces. Several things can improve bed adhesion on the Tevo Tarantula. If the first layer adheres, then the rest of the print will be easier. Several techniques and products are designed to enhance bed adhesion, ensuring prints stick firmly to the bed.
Using Adhesives and Build Surfaces
Applying adhesives or build surfaces can significantly improve bed adhesion. Common adhesives include glue sticks, hairspray, and specialized 3D printing adhesives. Glue sticks are great for PLA, while hairspray can work well for ABS. Build surfaces can also enhance adhesion. Build surfaces are designed to provide a better surface for the filament to stick to. Glass beds, coated with adhesives, are another popular option for the Tevo Tarantula. Some popular options include PEI sheets and build tak surfaces. These surfaces often provide excellent adhesion and make removing prints easier once they have cooled.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for ensuring good adhesion and longevity of the build surface. The build surface needs to be cleaned before each print. This involves removing any residue from previous prints and any dust or debris. For many surfaces, a simple wipe down with isopropyl alcohol (IPA) is enough to clean the surface. Always consult the build surface manufacturer’s guidelines for the best cleaning methods. Keeping the bed clean improves adhesion and prevents warping. It can also help to avoid nozzle clogs. Proper maintenance extends the life of your build surface.
Tip 5 Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with the best setup, you may still encounter problems. Troubleshooting is a necessary part of using ABL. Sensor issues, firmware configuration errors, and other factors can affect ABL performance. Learning to diagnose these problems will save time and frustration. When troubleshooting, it’s important to be methodical and to document each step. This will help you understand the problem, as well as how to fix it. When problems arise, you should understand how each part of the printer interacts and how they are all configured. Troubleshooting is an important part of 3D printing and auto bed leveling.
Sensor Not Triggering
If the sensor isn’t triggering, there are many things to investigate. First, make sure the sensor is connected to the mainboard properly. Verify the wiring connections and check the sensor’s power supply. Check the sensor’s detection range and make sure it’s set up correctly. In the firmware, confirm that the sensor is enabled and configured correctly. The sensor’s height needs to be set correctly, as well. Sometimes the sensor may be too high and will not trigger. Check to see if the sensor is compatible with the firmware. If the sensor is still not triggering, the sensor may be faulty and need to be replaced.
Bed Leveling Inconsistencies
Inconsistencies in bed leveling can lead to poor print quality, so they need to be addressed. Check the bed surface for any warping or imperfections. Make sure the bed is clean and free of debris. Check for any mechanical issues with the printer’s frame or bed supports. Recalibrate the Z-offset and the bed mesh. Ensure that the firmware is properly configured. It’s very important to use the correct parameters. If the bed leveling is still inconsistent, examine the ABL sensor. Is the sensor working correctly? Is it reliable? Is the sensor mounted securely? Performing these checks helps in identifying and correcting inconsistencies, which leads to improved print quality.
Advanced Tips and Tricks for Auto Bed Leveling
Fine-Tuning Z-Offset

Fine-tuning the Z-offset is crucial for the first layer, where it either succeeds or fails. Even with auto bed leveling, you will still likely have to adjust this setting to achieve the best results. After initial calibration, use the live Z-offset adjustment during the first layer to make small changes. If the nozzle is too far from the bed, the filament will not adhere. If the nozzle is too close, the filament will be squished too much. Adjust the Z-offset in small increments until the first layer looks perfect. Look for smooth, consistent lines with no gaps or excessive squishing. The goal is to find the “sweet spot” where the nozzle is the perfect distance from the bed.
Utilizing Mesh Bed Leveling
Mesh bed leveling allows the printer to compensate for bed imperfections. The sensor creates a mesh of data points across the bed surface, allowing the printer to adjust the nozzle height during printing. This feature will improve the overall print quality. To use it, enable mesh bed leveling in the firmware. Configure the grid size, which determines how many points the sensor probes. A finer grid can give you more accurate results, but it takes longer to probe. After enabling the mesh bed leveling, you should generate the mesh. Make sure to save these settings, so the printer remembers the mesh. This feature is an important tool for getting good prints.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Your Auto Bed Leveling System
Maintenance is an important part of keeping your auto bed leveling system in top condition. Inspect the sensor and its mounting hardware regularly. Over time, vibrations and wear and tear can loosen screws or damage the sensor. Clean the sensor lens or probe regularly to ensure accurate readings. A dirty sensor can affect the ABL’s performance. Keep the printer’s frame and bed level. Make sure the frame of the printer is square. Verify all of the wiring connections and look for any frayed wires. By performing regular maintenance and upkeep, you can extend the life of your ABL system and ensure it continues to produce great prints.