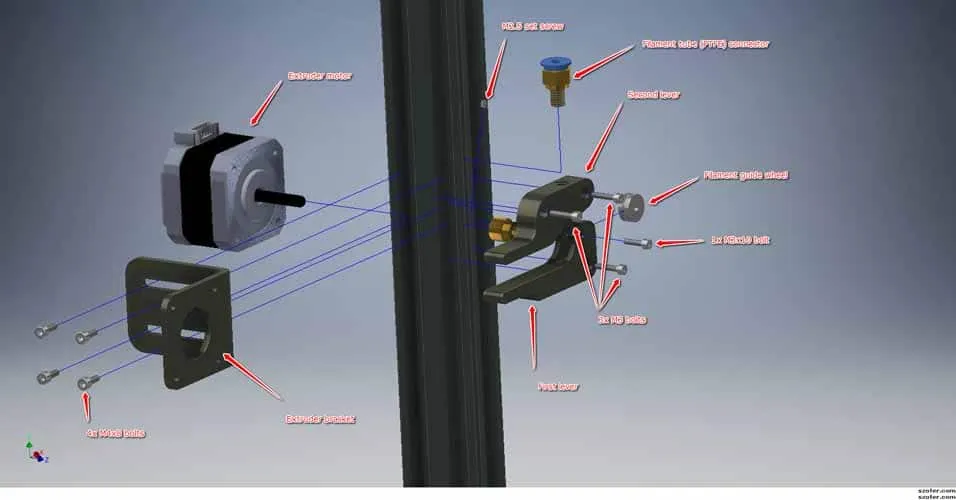
Understanding Filament Change on Tevo Tarantula
Changing filament on your Tevo Tarantula is a fundamental skill for any 3D printing enthusiast. It allows you to print with different colors, materials, and properties, opening up a world of creative possibilities. Whether you’re switching from PLA to ABS, or simply want to swap out a finished spool for a fresh one, understanding the process is essential. This guide provides actionable tips to help you change filaments efficiently and effectively, ensuring your prints come out perfectly every time. Mastering this technique can significantly enhance your 3D printing experience and reduce common print failures, making your projects smoother and more enjoyable. This comprehensive guide simplifies the process, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced users.
Why Filament Change Is Important
Filament change is important for several reasons. Firstly, it allows for multi-color prints, where different parts of your 3D model can be printed in various colors. This adds aesthetic appeal and functional differentiation to your prints. Secondly, changing filament lets you experiment with different materials. For example, you might start with PLA for ease of use and then switch to ABS for higher temperature resistance or PETG for its durability and flexibility. Thirdly, filament changes are necessary when a spool runs out mid-print. Knowing how to change filament mid-print can save your project from failure and minimize wasted materials. Regular filament changes also allow for maintenance and cleaning of the printer, preventing clogs and other common issues that can affect print quality.
Benefits of Changing Filament
The benefits of changing filament extend beyond mere aesthetics and material selection. It can significantly extend the lifespan of your printer components. Regularly changing filament gives you an opportunity to inspect the nozzle and hot end for any wear or blockages. This proactive approach can prevent more significant issues down the line, saving you time and money on repairs. Moreover, changing filament allows you to fine-tune your print settings based on the specific material being used, which improves the overall quality and precision of your prints. Whether you’re creating intricate models or functional prototypes, the ability to change filaments seamlessly ensures that you can adapt to your project’s specific needs. This versatility is crucial for maximizing the utility of your Tevo Tarantula 3D printer.
Materials and Tools Needed
Before diving into the filament change process, gathering the right materials and tools is crucial. Having everything ready at your fingertips will make the process smoother and more efficient. It will prevent you from having to pause mid-process to search for a tool, which can lead to print failures. The following sections detail the essential tools and materials needed to get started with filament changes on your Tevo Tarantula. Proper preparation is key to success. Ensuring you have all the necessary items readily available is the first step to a successful filament change.
Essential Tools for the Job
The essential tools for changing filament on your Tevo Tarantula are relatively simple, but each plays a crucial role. You will need a pair of flush cutters to trim the filament neatly, a nozzle cleaning tool, such as a needle or a specialized nozzle cleaner, for unclogging the nozzle if necessary, and a pair of tweezers to handle small parts or remove filament remnants. It is also advisable to have a heat-resistant silicone sock for the hot end, although this isn’t strictly essential. The sock helps to maintain a consistent temperature and prevent filament from sticking to the nozzle. Finally, a small brush to remove any debris from the print bed or the printer components is helpful for cleanliness. Make sure to have these tools available and in good condition for optimal performance.
Recommended Filament Types
Your Tevo Tarantula is compatible with a wide array of filament types. The most common and user-friendly is PLA (Polylactic Acid), ideal for beginners due to its low printing temperature and minimal warping. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is another popular choice, known for its strength and heat resistance, suitable for functional parts. PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol) offers a balance of flexibility, durability, and ease of printing. Other options include TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) for flexible prints and specialized filaments like nylon and carbon fiber composites for advanced applications. It is crucial to consult your printer’s specifications and the filament manufacturer’s recommendations for the correct temperature settings. Experimenting with different materials expands your printing capabilities and helps you find the best fit for your projects.
The Tevo Tarantula Filament Change Process Step by Step
The filament change process on the Tevo Tarantula involves several key steps. Each step must be followed carefully to ensure a smooth transition and a successful print. Skipping steps or rushing the process can lead to filament jams or print failures. This comprehensive step-by-step guide breaks down the process into manageable parts, providing you with a clear roadmap for changing your filament. Pay attention to each stage to guarantee the best results and to avoid common pitfalls. This detailed approach will help you change filament with confidence and ease, making your 3D printing projects more enjoyable.
Preheating the Nozzle
Before changing filament, preheating the nozzle is essential. Preheat your Tevo Tarantula’s nozzle to the recommended temperature for the current filament, typically around 200-220°C for PLA and 230-250°C for ABS. This heating softens the old filament inside the nozzle, making it easier to remove. The preheating process can be initiated via the printer’s control panel or through your slicing software. Ensure that the nozzle reaches the desired temperature before proceeding to the next step. Waiting for the nozzle to heat up properly ensures that the old filament melts sufficiently, facilitating a clean and efficient removal process, and preparing the printer for the new filament.
Removing the Old Filament

Once the nozzle is preheated, you can start removing the old filament. Use the printer’s control panel or slicing software to initiate the filament retraction function. This will pull the filament out of the hot end. If the filament doesn’t retract smoothly, manually assist the process by gently pulling the filament while the extruder motor is retracting. If the filament breaks off inside the hot end, use the needle tool to push the remaining filament out. It is also helpful to gently pull the filament while it’s still soft, to help the filament flow out from the nozzle. This part of the process requires careful attention to prevent damage to the hot end. Make sure the old filament is completely removed before loading the new one.
Loading the New Filament
After removing the old filament, the next step is loading the new one. Cut the end of the new filament at a 45-degree angle to create a clean, sharp tip. Insert the new filament into the extruder, ensuring that it feeds smoothly. Use the printer’s control panel or the slicing software to extrude a small amount of filament until the new color appears at the nozzle. Make sure there are no air bubbles or clogs during this process. This step is crucial to ensure that the new filament is fully loaded into the hot end and ready for printing. Watch carefully as the new filament extrudes to confirm it is flowing correctly, which helps ensure good print quality.
Adjusting Settings for New Filament
After loading the new filament, it’s crucial to adjust your print settings accordingly. Each filament type has different requirements for temperature, bed adhesion, and print speed. Refer to the filament manufacturer’s recommendations to find the ideal settings for the material you are using. Common adjustments include nozzle temperature, bed temperature, and first-layer adhesion settings. Fine-tuning these settings can significantly improve the quality of your prints. It’s advisable to run a test print, such as a calibration cube, to verify that the settings are correct before starting a large print. Make small adjustments and monitor the print quality until you achieve optimal results for your new filament.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Even with careful preparation, problems can arise during filament changes. Knowing how to troubleshoot these common issues can save you time and frustration. These troubleshooting tips provide practical solutions to resolve the most frequent problems encountered during filament changes. Being able to diagnose and fix these issues quickly can prevent failed prints and maximize your printing efficiency. It is essential to learn to identify and resolve common problems to maintain a smooth printing experience.
Filament Not Feeding Properly
If the filament doesn’t feed properly, it can be due to various reasons. Check that the extruder gear is properly gripping the filament. Make sure the filament isn’t tangled on the spool. Clean the extruder gear from any accumulated filament debris. Increase the nozzle temperature slightly to help the filament melt and flow more easily. If the filament still doesn’t feed, there might be a blockage in the hot end. In that case, use a nozzle cleaning tool to clear the obstruction. If none of these solutions work, inspect the PTFE tube in the hot end for damage or blockages. Make sure that the filament is correctly inserted and that there are no obstructions to its movement.
Nozzle Clogging
Nozzle clogging is a common issue that can halt your printing process. This can occur due to filament degradation, impurities, or improper temperatures. If the nozzle is clogged, first try preheating the nozzle to the filament’s recommended temperature. Then, manually push the filament through or use the retraction function to clear the blockage. Another method is using the needle tool to insert into the nozzle. If the clog persists, consider performing a “cold pull” where you heat the nozzle, manually push filament through, and then cool it down, pulling the filament out to remove the clog. You may also need to disassemble the hot end and clean it thoroughly. Regular maintenance and monitoring of your filament quality can help prevent clogs.
Bed Adhesion Problems

Poor bed adhesion can cause prints to fail early in the process. Ensure the print bed is level and clean before starting a print. Applying a thin layer of glue stick, hairspray, or blue painter’s tape can improve adhesion, especially for materials like ABS. Adjust your first-layer settings such as the nozzle height and initial print speed to optimize bed adhesion. Also, ensure that the bed temperature is correct for the filament you are using. For instance, PLA typically benefits from a bed temperature of around 60°C. Regularly clean the print bed and recalibrate the level to prevent adhesion problems. Proper bed adhesion is crucial for ensuring the success of your prints, so these steps are very important.
Post Filament Change Tips
After successfully changing your filament, there are several things you can do to optimize print quality and maintain your Tevo Tarantula. These additional tips will help you maintain the printer and improve the quality of your prints. By following these guidelines, you can ensure your 3D printing experience is consistently positive and productive. Proper maintenance is vital for the longevity of your printer and the quality of your prints.
Optimizing Print Settings
Once the filament change is complete, fine-tuning the print settings is crucial. Every filament type and even different colors from the same manufacturer may require slight adjustments. Optimize your print speed, layer height, and infill to achieve the desired results. Experiment with different retraction settings to minimize stringing and improve print quality. Consider using software like Cura or Simplify3D to generate detailed print profiles specific to each filament, further improving your results. Monitor the print’s progress and make small adjustments as needed to fine-tune the settings. Doing this consistently will lead to high-quality prints that are more reliable and efficient.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance are essential for keeping your Tevo Tarantula running smoothly. After each filament change and regularly, clean the print bed with isopropyl alcohol to remove any residue and ensure good adhesion. Use a brush to remove any filament debris. Periodically lubricate the printer’s moving parts, like the rods and lead screws, to reduce friction. Inspect the belts and pulleys for wear and tear. If your nozzle frequently clogs, consider disassembling and cleaning the hot end thoroughly. Keeping your printer clean will enhance its performance and reduce the likelihood of print failures. This practice contributes significantly to the printer’s reliability and lifespan.
Conclusion
Changing filament on your Tevo Tarantula is a straightforward process when approached with the right knowledge and tools. By following the tips outlined in this guide, you can seamlessly transition between filaments, explore different materials, and enhance the quality of your 3D prints. Remember to always prioritize safety, preheat the nozzle, and adjust your print settings accordingly. With practice and patience, you will become proficient at filament changes. This skill will unlock new levels of creativity and functionality in your 3D printing projects, opening the doors to a world of possibilities. By focusing on the details, you can create high-quality prints consistently.